Have you ever wondered why some of your website pages aren’t showing up on Google search results? It can be frustrating to put in the time and effort to create quality content only to find out it’s not getting the visibility you want. There are several reasons why pages might not be indexed in Google, and in this article, we’ll go over each one in detail.
Firstly, its important to note that its not always a bad thing that pages aren’t indexed by Google. In fact there are often a number of very good reasons why you wouldn’t want a page to be indexed. Throughout the article we’ll cover the “good” and “bad” reasons why a page not being indexed can impact your site and how to address each one.
Before we do that however, let’s discuss how you can check which pages aren’t indexed in Google using Google Search Console. Google Search Console is a free tool that allows you to monitor your website’s performance in search results. Once you’ve implemented Search Console and verified your website, navigate to the ‘Pages’ report, and you’ll be able to see any issues that Google has found on your site. From here, you can identify any pages that are not indexed, and start to diagnose the problem.
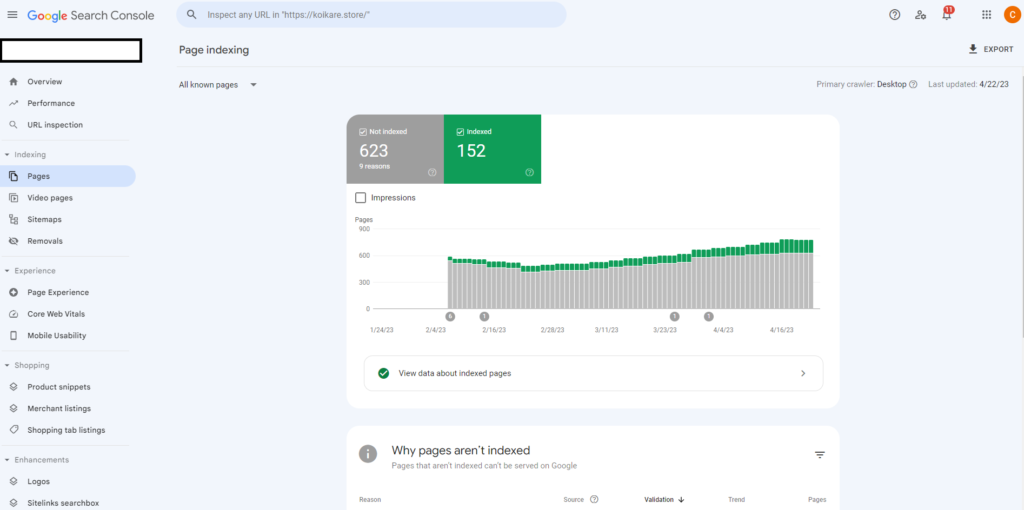
Conveniently, Google provide a good summary of the reason pages aren’t indexed.
Now, let’s dive into the different reasons why pages might not be indexed in Google.
1. Page With Redirect:
A page with redirect is a page that, when accessed, automatically sends the user to a different page. Redirects are often used when a website undergoes structural changes, such as a URL change, or when pages are merged or deleted. However, if a page with redirect is not implemented correctly, it can cause issues with indexing.
When Googlebot crawls a page with a redirect, it will usually follow the redirect and index the new page. This means that the original page may not be indexed, and users searching for that content may not be able to find it. This can lead to a decrease in traffic to your site.
To solve a page with redirect issue, you need to ensure that the redirect is implemented correctly. Firstly, make sure that the redirect is necessary and not a mistake. Check to see if the redirect is sending the user to the correct page, and that the new page contains the same or similar content to the original page. If the redirect is incorrect or unnecessary, you should remove it.
If the redirect is necessary, ensure that it is a 301 redirect. A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that tells search engines that the original page has permanently moved to a new location. This will ensure that Google indexes the new page and passes the link equity from the original page to the new page. It’s important to note that a 302 redirect, which is a temporary redirect, will not pass link equity and may cause issues with indexing.
Once you’ve implemented a 301 redirect, you should also update any internal links that point to the original page to point to the new page. This will ensure that users are directed to the correct page and that the link equity is passed correctly.
A page with redirect is not necessarily a bad thing for your website, however it is important to ensure it is implemented correctly to minimise the impact on user experience, maximise link equity and minimise 404 errors.
2. Not Found (404)
A “Not Found” (404) error occurs when a page cannot be found on the server. This can happen if the URL is incorrect, the page has been deleted, or there is an issue with the server. If a page returns a 404 error, it will not be indexed by Google. To solve this issue, you should ensure that the URL is correct and that the page is accessible on the server. If the page has been deleted, consider redirecting users to a relevant page on your site using a 301 redirect as covered above.

3. Alternate Page With A Proper Canonical Tag
If you have multiple versions of a page on your website, Google may not index all of them. Instead, it may index the version with a proper canonical tag in place. A canonical tag tells search engines which version of the page is the preferred one to index. By using a canonical tag, you can avoid duplicate content issues and ensure that the correct page is indexed. If a page is being indexed that you would expect to not be in could be that in some instances Google will ignore canonical tags or it has not been implemented correctly.
4. Soft 404
A soft 404 error is when a page returns a 200 status code instead of the expected 404 status code, which implies that the page exists when it actually does not. This can happen when a website returns a generic error page instead of a specific 404 error page. Soft 404 errors can cause confusion for users and search engines, and they may not be indexed by Google. To solve this issue, you should ensure that your website returns the correct 404 error page when a page cannot be found. This will help users understand that the page does not exist and help search engines correctly index your website.
5. Excluded By ‘No Index’ Tag:
When a page has a “no index” tag, it tells search engines not to index the page. This can be useful in certain cases, such as when you have a page that contains duplicate content, or when you have a page that you don’t want to appear in search results. If you see a page here that you didn’t expect it has likely had a no index tag applied in error. Typically this can be managed in your CMS (see the below example using Yoast SEO plugin for WordPress).

If you cannot find this option within the CMS it can also be removed directly in the page HTML which is typically in the header. It’s important to note that once a page has been re-crawled and re-indexed, it may take some time for the changes to take effect in search results.
6. Duplicate Without User-Selected Canonical
A duplicate content issue can occur when multiple pages on your website have the same or similar content. This can confuse search engines, which may not know which page to index or may choose to index the wrong page. If the duplicate content issue is not addressed, it can negatively impact your website’s search engine rankings.
One way to address duplicate content is to use a canonical tag. A canonical tag tells search engines which version of a page is the preferred version to index. If you have multiple pages with the same or similar content, you can add a canonical tag to the page header to indicate which page you want search engines to index. However, if there are duplicates without a user-selected canonical, it means that the search engine is unable to determine which page to index.
7. Blocked By Robots.txt
The robots.txt file is a file that tells search engines which pages or sections of your website should not be crawled or indexed. If a page is blocked by the robots.txt file, search engines will not be able to access it, and therefore, it will not be indexed. If you see a page here that you believe shouldn’t be blocked you should check your robots.txt file to see which rules are in place.
To remove the block, you need to edit the robots.txt file to allow search engines to crawl and index the page. This can be done by removing the rule that is blocking the page or by adding a new rule that allows search engines to access the page. Once the change has been made, you should request that Google re-crawls and indexes the page using the Google Search Console tool.
8. Duplicate Google Chose Different Canonical Than User
Linked to the other canonical index types already highlighted in the article this type is given when Google determines that a different version of the page is more relevant or has better quality signals than the user-selected canonical version. As you can imagine, this is a bit of a challenge of an issue because not only is Google semi-ignoring the canonicals it is also deeming another page on the site to be higher in quality than the page you chose.
If the user-selected canonical is the best version of the page, you can try to improve the page’s quality signals, such as improving the content, user experience, or backlinks, to make it more relevant to users and search engines. You can also add structured data or metadata to the page to help search engines understand its content and relevance. But unfortunately there is no guarantee that Google will take notice of this. Therefore the best strategy could be to switch focus to the page Google has chosen to index and build content and change existing canonicals to build authority on the new page.
9. Crawled – Currently Not Indexed
“Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” is a status in Google Search Console that means Googlebot has crawled the page, but has not yet indexed it. This can happen if the page is new or if Google’s index is busy. If a page is not indexed, it will not appear in search results. To try and solve this issue you should ensure that a page’s content is high-quality, unique and relevant to users. You should also ensure that the page is structured properly with a clear hierarchy and headings. Finally check there are no technical issues with the page. We previously covered this topic in its own article, if you are looking for more detail on this issue we suggest reading our guide to discovered not currently indexed.
Unfortunately there is no quick fix and no guarantee to how this can be solved. Our biggest recommendation is to ensure the pages affected as well as the entire website are optimised, provide high quality content and a good, relevant user experience. When this is done you can request Google re-crawls and indexes within Search Console. Be aware however that this can take quite some time to be completed and again there are no guarantees it will be solved.
10. Discovered – Currently Not Indexed
“Discovered – Currently Not Indexed” means Googlebot has discovered the page but has not yet indexed it. This can happen if the page is new or if it has undergone significant changes that Google has not yet processed.
Similar to Crawled – Currently Not Indexed the best advice for this is to continue to work on page quality, ensure there are no technical issues with the page and optimise the meta information. When this is done you can request for Google to re-crawl the website. However, similar to above there is no guarantee on when this will be done and if it will solve the problem.
It’s also important to note that sometimes Google may choose not to index a page even if it is of high-quality and properly optimised. This could be due to a number of factors, such as competition from similar pages, lack of relevance, or insufficient link signals. In these cases, you may need to revisit your content strategy and consider other ways to promote your website.
11. Server Error (5xx)
A server error (5xx) in Google Search Console means that Googlebot was unable to access a page on your website due to a server-side error. This could be due to a number of factors, such as a temporary outage, a misconfigured server, or a database error. Server errors can negatively impact your website’s search engine rankings and visibility.
There are several different types of server errors, including:
- 500 Internal Server Error: This error occurs when the server encounters an unexpected condition that prevents it from fulfilling the request.
- 502 Bad Gateway: This error occurs when the server acting as a gateway or proxy receives an invalid response from the upstream server.
- 503 Service Unavailable: This error occurs when the server is temporarily unable to handle the request due to maintenance or overload.
To solve this issue you should work with your web hosting provider or IT team to diagnose and fix the server error. This may involve checking the server logs for error messages, troubleshooting any misconfigured settings, or addressing any issues with the server hardware.
Once the server error has been fixed, you should request that Google re-crawls and indexes the affected pages using the Google Search Console tool. This will prompt Google to re-crawl the pages and ensure that they are properly indexed in search results.
12. Redirect Error
A ‘Redirect Error’ means that Googlebot was unable to follow a redirect from one page to another on your website. This could be due to a number of factors, such as a misconfigured redirect, a broken link, or an incorrect HTTP status code. Redirect errors can negatively impact your website’s search engine rankings and visibility.
There are several different types of redirect errors, including:
- 301 Moved Permanently: This redirect indicates that the page has permanently moved to a new location.
- 302 Found: This redirect indicates that the page has temporarily moved to a new location.
- 307 Temporary Redirect: This redirect indicates that the page has temporarily moved to a new location.
- 308 Permanent Redirect: This redirect indicates that the page has permanently moved to a new location.
Once you have identified the pages, you should evaluate the redirect settings and ensure that they are properly configured. This may involve checking the HTTP status codes, updating the redirect URLs, or addressing any broken links.
Conclusion
Once the redirect errors have been fixed, you should request that Google re-crawls and indexes the affected pages. This will prompt Google to re-crawl the pages and ensure that they are properly indexed in search results.
In conclusion, there are several reasons why pages might not be indexed in Google, but with the right tools and knowledge, you can diagnose and fix the issue. By regularly monitoring your website’s performance in Google Search Console, you can ensure that your content is getting the visibility it deserves. Contact us today if you need any further help with any Search Console indexing issues.
